How You Can Detect Beginning Stages Of Gingivitis
|
Time to read 4 min
|
Time to read 4 min
Gingivitis is a very common and mild type of gum disease (periodontal disease) that can cause inflammation and redness as well as swelling (inflammation) within your gingiva. It's the port of your gums around the tooth's base. It is important to treat carefully and immediately. Gingivitis could lead to more severe gum disease, known as periodontitis, and even tooth loss.
The leading reason for gingivitis is bad oral hygiene. A healthy oral hygiene routine , including brushing twice a day and having regular dental checks, will help to stop and reverse gingivitis.
But now the question is how you can detect the beginning stages of gingivitis. And what are the signs and symptoms of gingivitis?
No need to worry! We will discuss all the details about the gingivitis symptoms and treatment that will help you to deduct the Gingivitis problems and its stages.
Gingivitis is one of the early stages of gum disease ( periodontal disease ). It occurs when bacteria, tartar, and plaque accumulate over the surface of your teeth and cause swelling, redness, and bleeding gums.
It is possible to manage gingivitis successfully by utilizing the aid of a dental practitioner. If left untreated, the condition can cause periodontitis (a more severe form of gum disease that involves loss of jaw bone).
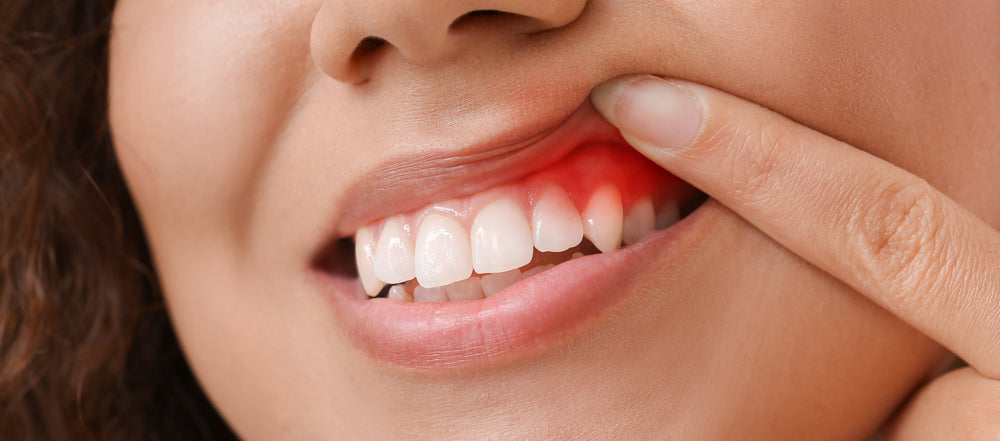
At the beginning stage of gingivitis, you will notice swelling, redness, gum recession, plaque buildup as well as bad breath. The gums may also be bleeding when you floss or brush.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis?
Healthy gums are soft and pale pink. They are also tight around the teeth. The signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
If your doctor suspects you have a gum infection, dental X-rays will reveal if the condition has affected your jawbone beneath.
Read More About: Gum Disease Treatment Linked To Improvements In Other Conditions
How is Gingivitis Treated?
The treatment of gingivitis is designed to stop the condition and ensure that your gums and teeth are healthy. The dentist or periodontist you choose to consult will meticulously clean your teeth in order to remove harmful plaque, tartar, and bacteria. Other treatments for gingivitis include:
Scaling and root planning: The treatment is similar to routine dental cleaning, but it reaches deep beneath the gums. Scaling is a way to remove tartar and other bacteria. The process smooths the surfaces of your tooth roots and helps prevent bacteria from sticking to your teeth.
Improved dental hygiene: A regular dental cleaning typically eliminates gingivitis. However, you must maintain your hygiene after you have returned home. You'll be taught how to take care of your teeth and also get assistance scheduling your checkups.
Antimicrobial mouthwash: Rinsing your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash may aid in the destruction of harmful bacteria.
Effective bad breath remedies include:
Gentle and regular scraping of the tongue
Regular oral care practices such as daily brushing and flossing
Professional deep cleanings and plaque removal
The ongoing use of oral probiotics.
One, the probiotics compete with the existing bad bacteria and reduce their presence by “crowding them out”
Two, the probiotics produce BLIS or “bacteriocin-like-inhibitory-substances” which is a technical way of stating that one probiotic strain (bacteria) can produce a substance that inhibits or kills off other bacteria. Three, by working to control gingivitis, gum disease and tooth decay these probiotics reduce the very sources of bacteria-generated odors in the mouth.
Studies have shown a clear reduction in plaque levels and gingivitis symptoms when oral probiotics were administered to patients with moderate to severe gingivitis.


